Overview
This walkthrough documents my experience completing the Enumeration & Brute Force room on TryHackMe. The room provides hands-on experience with various enumeration techniques, brute force attacks, and web application vulnerability exploitation. This write-up details my approach to each task and the key learning points along the way.
Task 1: Introduction
The introduction task provides an overview of what we’ll be learning in this room. No answers are required for this section, but it sets up important context for the upcoming challenges.
Key topics covered in this room include:
- Authentication enumeration techniques
- User enumeration methodologies
- Password reset vulnerabilities
- HTTP Basic Authentication exploitation
- OSINT (Open Source Intelligence)
Task 2: Authentication Enumeration
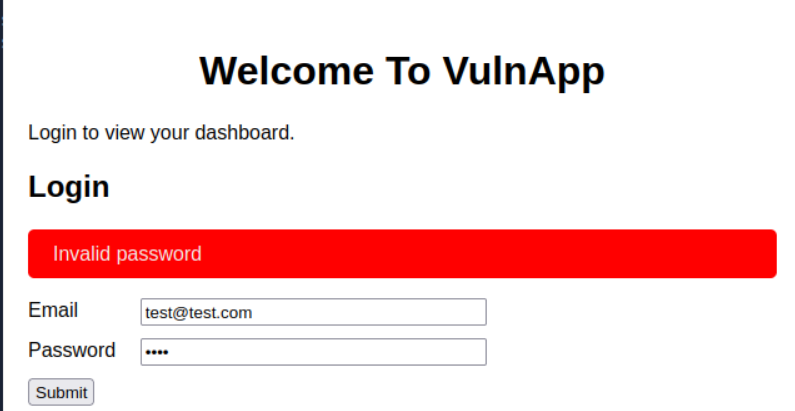
This task introduces the concept of authentication enumeration and how seemingly harmless error messages can provide attackers with valuable information.
Question: What type of error messages can unintentionally provide attackers with confirmation of valid usernames? Answer: Verbose errors
Explanation
Verbose error messages are a common security misconfiguration that can leak sensitive information. When a system provides different error messages for:
- Invalid username: “User does not exist”
- Valid username but wrong password: “Incorrect password”
This differential response allows attackers to enumerate valid usernames by observing the error messages.
Task 3: Enumerating Users
This task provides practical experience with user enumeration techniques using actual tools and methodologies.
Question: What is the valid email address from the list? Answer: canderson@gmail.com
Methodology
- Started with a common username list from GitHub
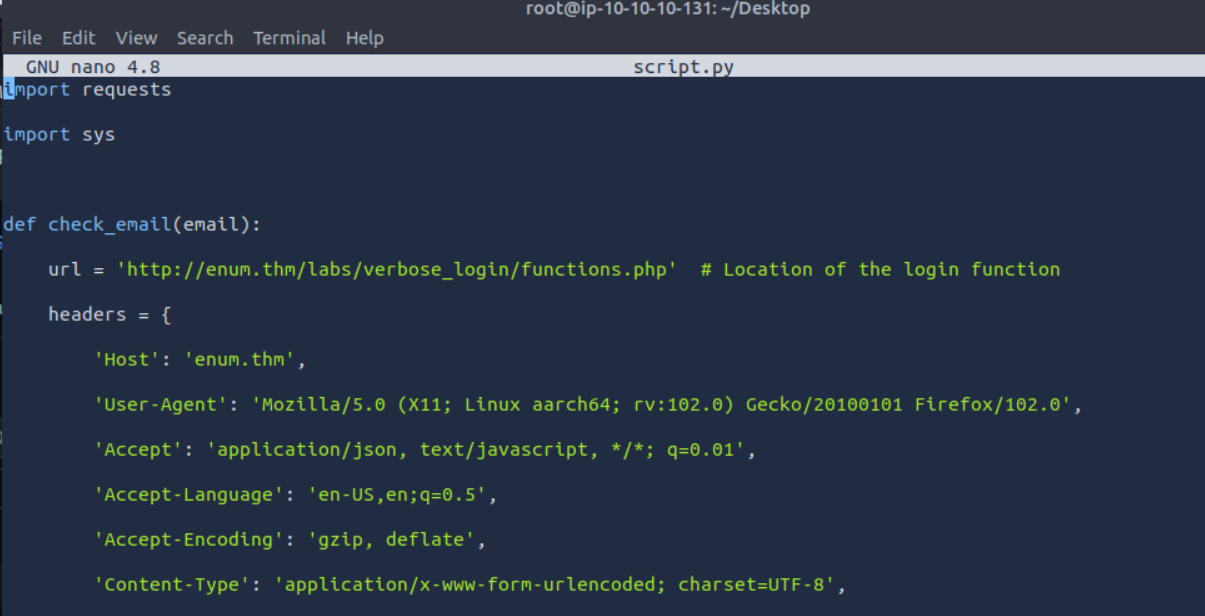
- Analyzed server responses for different usernames
- Identified patterns in error messages
- Located the valid email address through response analysis
Task 4: Exploiting Vulnerable Password Reset Logic
This section explores common vulnerabilities in password reset functionality and how they can be exploited.
Question: What is the flag? Answer: THM{50_pr3d1ct4BL333!!}
Exploitation Process
- Analyzed the password reset functionality
- Identified predictable reset token patterns
- Developed a methodology to exploit the vulnerability
- Retrieved the flag after successful exploitation
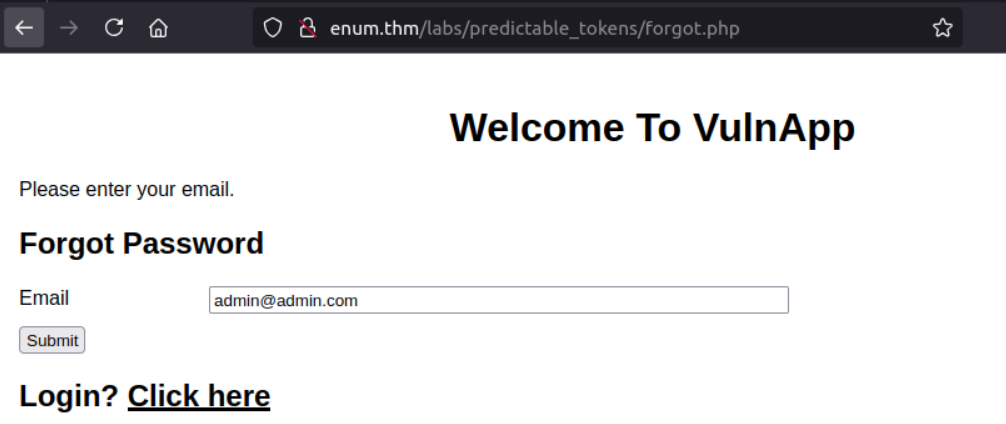
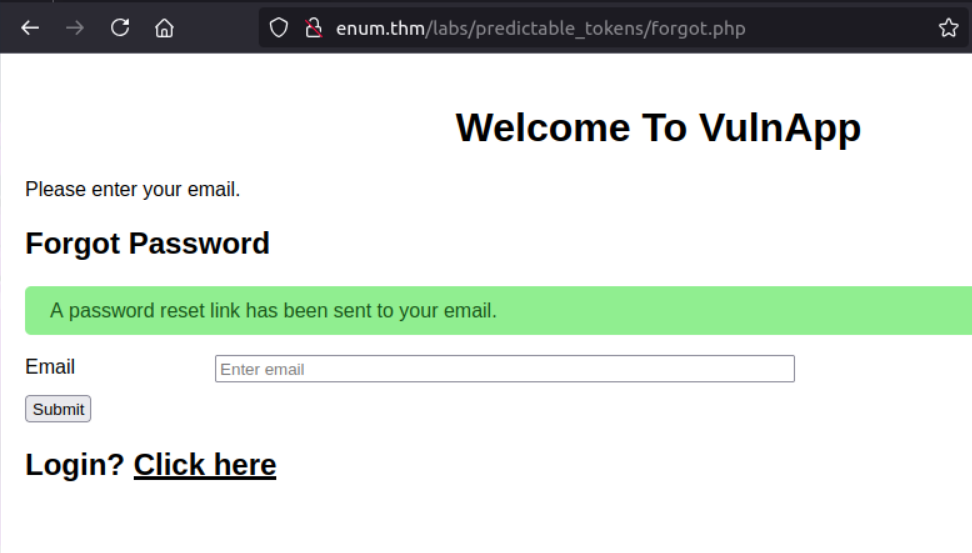
Task 5: Exploiting HTTP Basic Authentication
This task focuses on exploiting vulnerabilities in HTTP Basic Authentication implementations.
Question: What is the flag? Answer: THM{b4$$1C_AuTTHHH}
Attack Methodology
- Identified the Basic Authentication mechanism
- Analyzed potential weaknesses
- Developed and executed exploitation strategy
- Successfully retrieved the flag
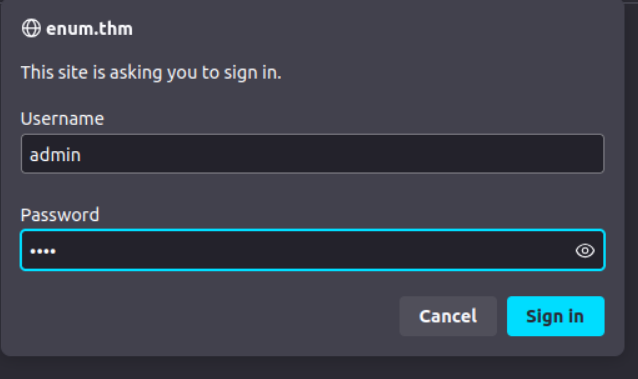
Task 6: OSINT
The OSINT task introduces techniques for gathering information from publicly available sources. While no specific answers were required, this section provided valuable insights into:
- Social media reconnaissance
- Public data source analysis
- Information correlation techniques
- OSINT tool usage
Task 7: Conclusion
This room provided comprehensive hands-on experience with various enumeration and brute force techniques. Key takeaways include:
- The importance of proper error message handling in authentication systems
- Understanding common vulnerabilities in password reset mechanisms
- Proper implementation of HTTP Basic Authentication
- The role of OSINT in security assessments
- Best practices for preventing enumeration attacks
Defensive Recommendations
- Implement generic error messages
- Use secure password reset mechanisms
- Properly configure authentication systems
- Regular security assessments
- Employee security awareness training
If you’re interested in trying this room yourself, you can find it on TryHackMe.
Additional Resources
- OWASP Authentication Cheat Sheet
- OWASP Brute Force Attack Prevention
- Port Swigger Web Security Academy
Remember: This knowledge should be used ethically and legally, preferably in controlled environments like TryHackMe rooms or with explicit permission.


