Walkthrough of the Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) room on TryHackMe, part of the Jr. Web Penetration Tester learning path.
🧭 Access the TryHackMe IDOR Room — Complete this room to practice real-world exploitation of Insecure Direct Object References in a safe lab environment.
Task 1: What is an IDOR?
Q: What does IDOR stand for?
A: Insecure Direct Object Reference
IDOR occurs when an application exposes a reference to an internal object (e.g. file, user ID, invoice number) without checking that the user is authorized to access it.
Task 2: An IDOR Example
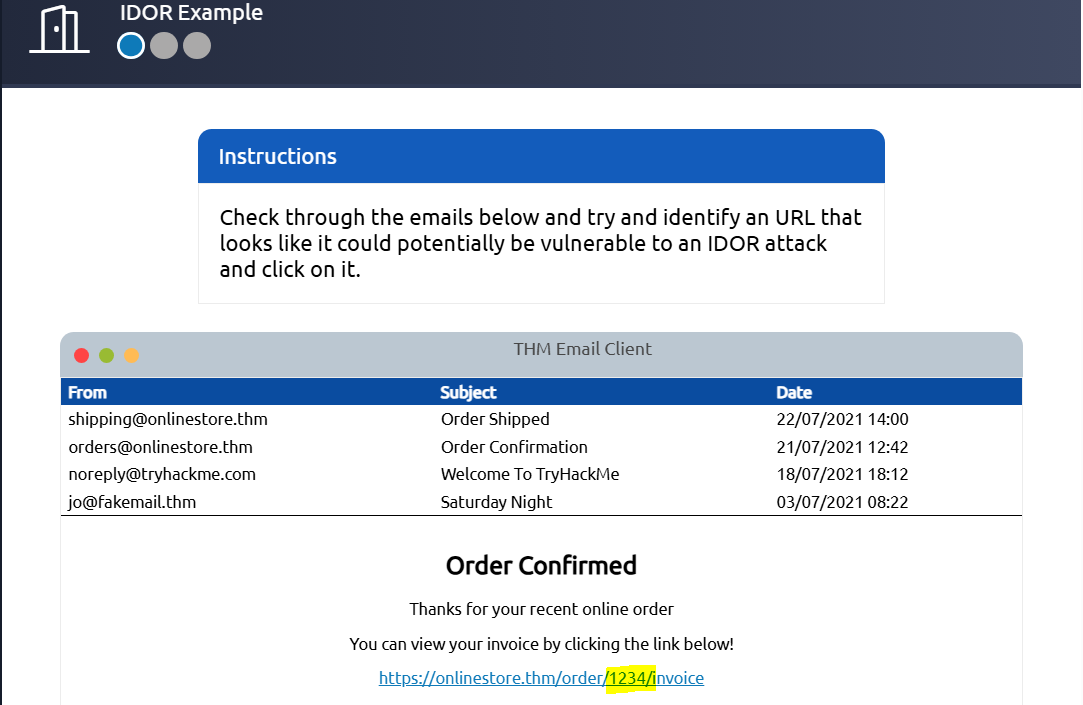
In this task, we find an invoice URL in an email:
https://onlinestore.thm/order/1234/invoice
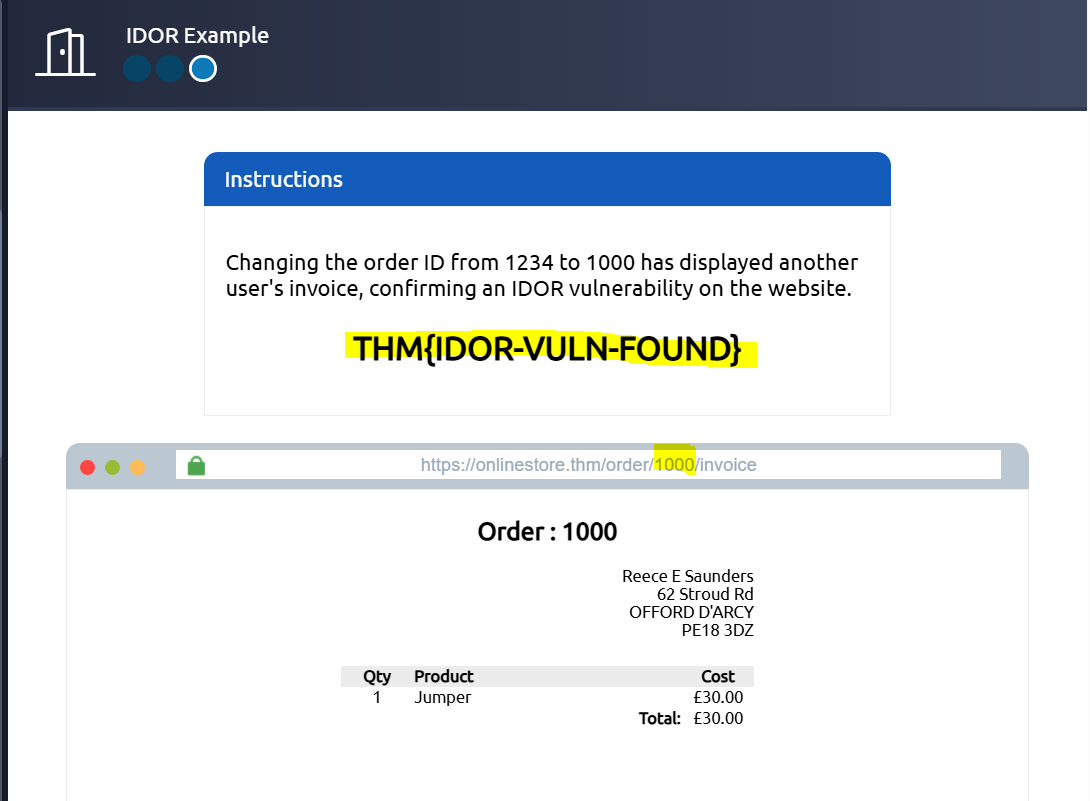
Modifying the 1234 ID to 1000 revealed another user’s invoice.
Flag:
THM{IDOR-VULN-FOUND}
Task 3: Finding IDORs in Encoded IDs
Q: What is a common type of encoding used by websites?
A: base64
Common technique:
- Look for =, ==, or suspicious long strings.
-
Decode with:
echo MTIzNA== base64 -d
Task 4: Finding IDORs in Hashed IDs
Q: What is a common algorithm used for hashing IDs?
A: md5
Example:
GET /invoice?id=c4ca4238a0b923820dcc509a6f75849b
echo -n "1" | md5sum
Useful Tools:
- Burp Suite Repeater
- CyberChef
- CrackStation
- Linux CLI: md5sum
Task 5: Finding IDORs in Unpredictable IDs
Q: What is the minimum number of accounts you need to create to check for IDORs?
A: 2
Create two accounts and test access to resources created by one from the other.
Task 6: Where Are IDORs Located?
IDORs can be found in the following locations:
Common Locations Checklist
- URL / Query Parameters – ?id=123
- Form Data – user_id=123
- HTTP Headers – X-User-ID: 123
- Cookies – user_id=123
- API Endpoints – /api/v1/customer?id=123
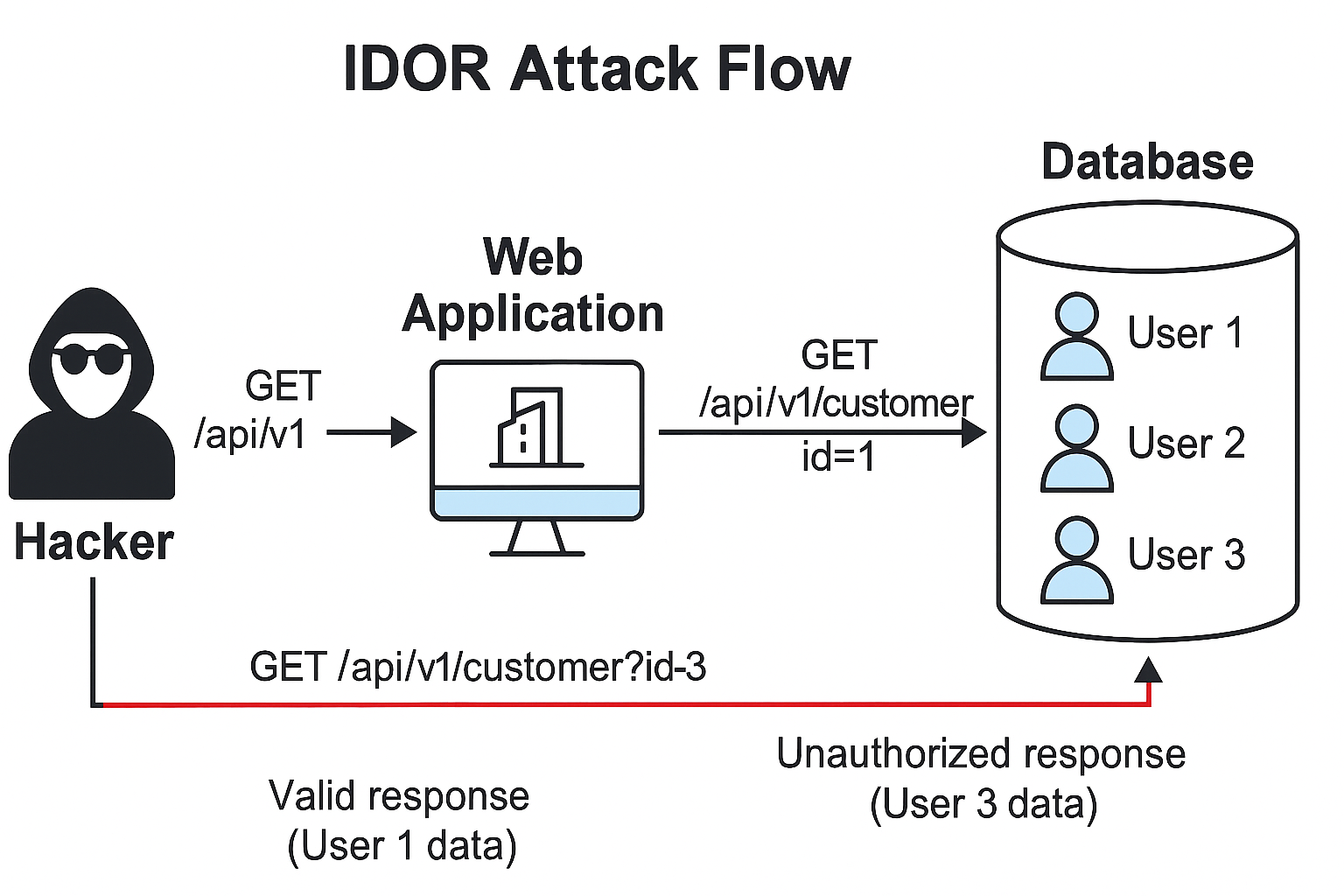
Task 7: A Practical IDOR Example
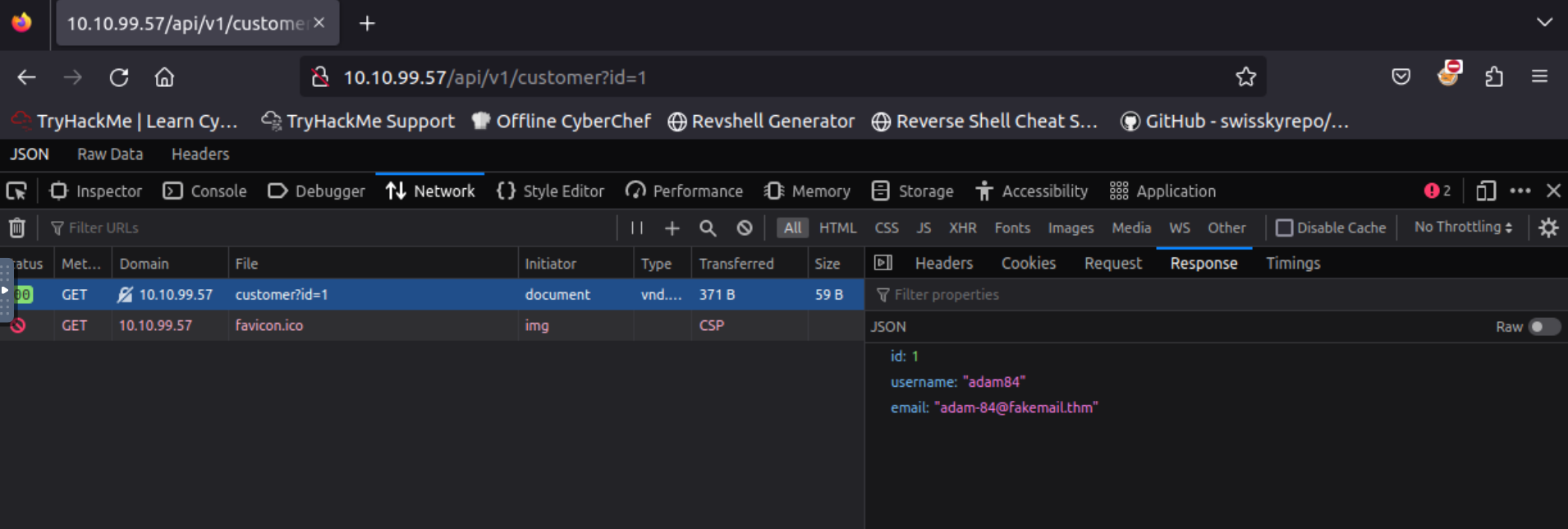
The following API call returns user info:
GET http://10.10.99.57/api/v1/customer?id=1
Response:
{
"id": 1,
"username": "adam84",
"email": "adam-84@fakemail.thm"
}
Q: What is the username for user id 1?
A: adam84
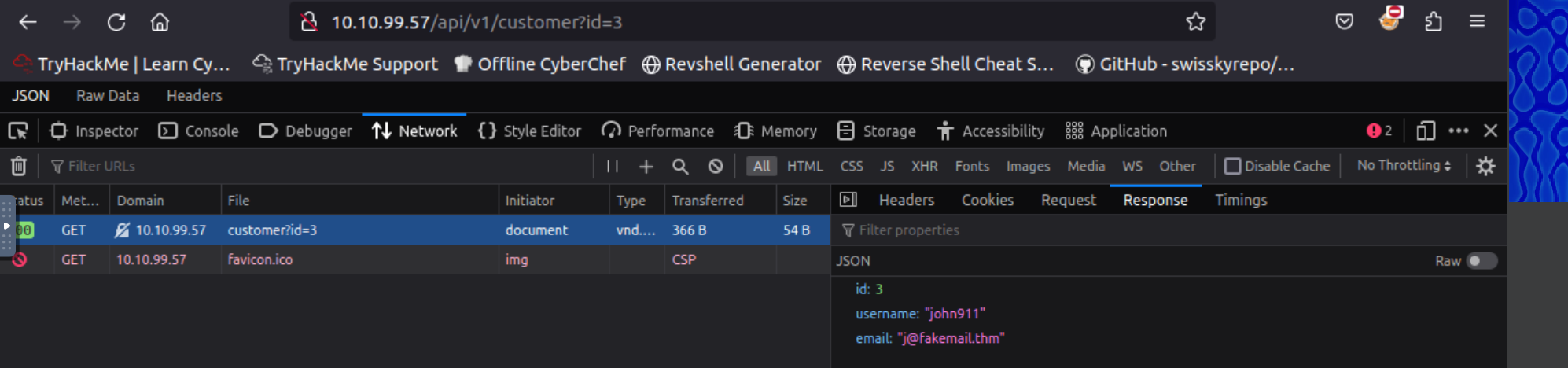
Testing another ID:
GET http://10.10.99.57/api/v1/customer?id=3
Response:
{
"id": 3,
"username": "john911",
"email": "j@fakemail.thm"
}
Q: What is the email address for user id 3?
A: j@fakemail.thm
API-Based IDOR Testing Checklist
Steps
- Discover API endpoints using dev tools or proxy.
- Modify predictable IDs (1, 2, 3…).
- Check if access control is enforced.
- Use Burp, Postman, or scripts.
- Document unauthorized access and impacted data.
Visual Summary
Conclusion
This room reinforced several key lessons:
- Understanding and identifying IDOR vulnerabilities.
- Testing predictable and encoded identifiers.
- The importance of proper authorization checks on all sensitive endpoints.
Thanks for reading!!
- NotesByNisha